1.
Theorem 1: Let
n be fixed positive integer. Two integers a and b are said to be
congruent modulo n, symbolized by
)
if
n divides the difference a -b; that is provided that
a-b = kn for some integer
k. Example
)
2.
Theorem 2: Let
n > 1 be fixed and
a, b, c, d be arbitrary integers. Then the following properties hold
(a) a

a (mod n)
(b) If a

b (mod n), then b

a (mod n)
(c) If a

b (mod n) and b

c (mod n), then a

c (mod n)
(d) If a

b (mod n) and c

d (mod n), then a +c

b + d (mod n) and ac

bd (mod n)
(e) If a

b (mod n), then a + c

b + d (mod n) and ac

bd (mod n)
(f) If a

b (mod n), then
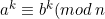)
for any positive integer k